DENTAL BRIDGES
These are prosthetic devices that replace are meant to replace teeth that have been extracted due to decay, damage or other reasons. The absence of one or a number of teeth can affect the functionality of your smile and change your appearance apart from other effects such as, shifting of remaining teeth, change in occlusion, temporomandibular joint disorder (TMJ), speech defects, increase in risk of periodontal disease and tooth decay. It would also make you self-conscious. However, a number of ways exist to fix your smile so fear not.
There are a few types of permanent dental bridges including conventional bridge and cantilever.
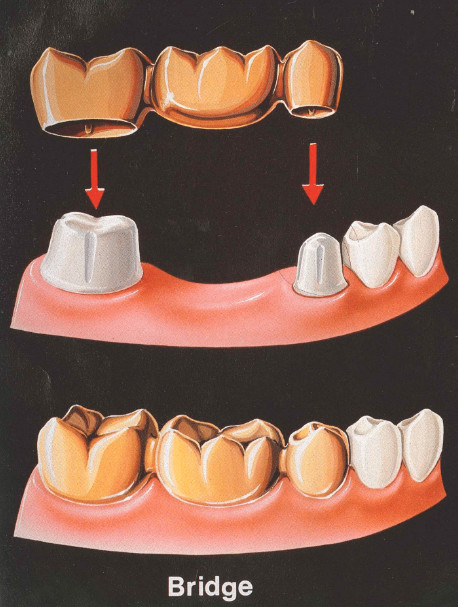
Before a cantilever or conventional bridge can be placed the teeth adjacent, to the empty tooth socket, will have to be re-shaped. The crowns will then be placed on the shaped teeth and connected to an artificial tooth, called a pontic.
CONSULTATION AND TREATMENT PLANNING
Your dentist will examine you and determine which type of bridge would be a suitable replacement for your missing tooth or teeth. There are a number of different materials that can be used to manufacture your bridge. The type of material chosen will be based on a few facts such as, whether you clench or grind your teeth (bruxism), dental insurance coverage and various other factors as advised by your dentist.
Nowadays you have an option of getting your prosthetic fabricated by using a combination of porcelain and metal, gold and porcelain or exclusively with metal-free, high-strength material like zirconia or alumina.
The treatment process will start off with your dentist taking x-rays, impressions of the area to be treated and preoperative photographs in order to determine the most suitable restoration for you.
He will then suggest the type of bridge. It can contain 3 or more units, 2 crowns cemented to teeth on each side of the empty socket (called abutments), and one or more false teeth (called pontics) depending on the number of consecutive teeth you are missing. More impressions will be obtained after the abutment teeth are prepared.
CANDIDACY AND PROCEDURE DETAILS
At the initial visit, your dentist will evaluate the health of your gums and other teeth to determine if you are a good candidate for a bridge. He will then go on to prepare the teeth required to support the bridge. A local anesthetic will be used to numb the area for the procedure. If the support teeth are badly damaged or decayed, your dentist will have to build them up and strengthen them before they can be used to support the prosthetic.
Impressions of the prepared teeth will be obtained, with a material similar in texture to putty, to create a model. A skilled lab technician will use this to fabricate your bridge to fit the prepared teeth flawlessly.
This is very important as a perfect fit will prevent additional oral health issues like tooth decay and damage resulting from an ill-fitting prosthetic.
Your dentist will fit you with a temporary prosthetic while the permanent one is being fabricated; this will help protect your 'prepared' teeth and gums in the meanwhile.
Once the bridge is ready you will have to go to your dentist to get it fitted in and cemented in place flawlessly. This is an important step.
RECOVERY AND POST-PROCEDURE CARE
Your dentist will advise you on how to maintain good oral hygiene after the permanent bridge is cemented in place. This is vital to maintain performance and longevity of the bridge along with the health of your teeth and gums. Brush your teeth at least twice a day with fluoridated toothpaste, floss the areas surrounding the bridge daily, in between the pontics, the gums and beneath them thoroughly to prevent the build-up of plaque and bacteria which can be damaging to your teeth.
WHAT ARE THE BENEFITS OF DENTAL BRIDGES?
Bridges serve to:
- Improve the ability to properly chew, speak and smile.
- Prevent the remaining teeth from getting out of position.
- Distribute the forces in your bite symmetrically by replacing the missing teeth.
- Maintain your face shape.
WHAT TYPES OF DENTAL BRIDGES ARE AVAILABLE?
Bridges are of two types:
- Traditional bridges – these are the most common types and are made of ceramics orporcelain-fused-to-metal. It includes a crown for the tooth or implant on either side of the missing tooth with pontics in between.
- Canteliver bridges – are not commonly used and are not recommended being used in the back of the mouth where it can put increased force on the other teeth resulting in damage. These bridges can be used when adjacent teeth are found only on one side of the missing tooth or teeth.
THE PROCESS OF GETTING A DENTAL BRIDGE
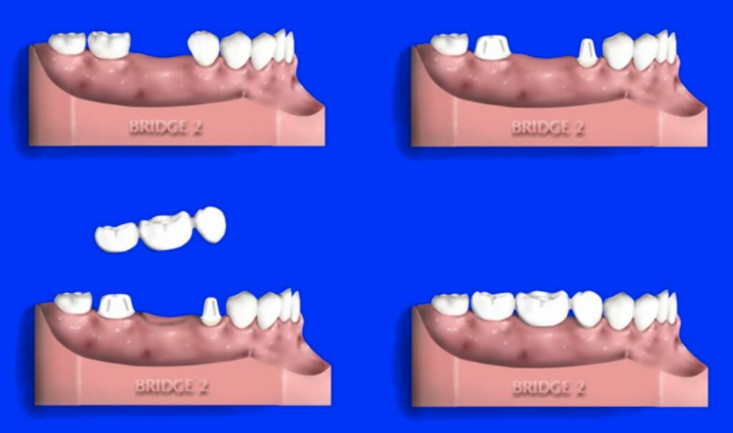
- At the initial visit to the dentist, abutment teeth are prepared by re-contouring them. This is done by removing a part of the enamel in order to make room for the crown to be place over them.
- Impressions of the teeth are obtained, which will be used as the model for the fabrication of the bridge, pontics and crowns.
- A temporary bridge will be fitted in place to protect the exposed teeth and gums, until the permanent prosthetic is ready.
- At the second visit, the temporary one will be taken out; the new one (made of either metal or porcelain) will be adjusted and checked to determine if it is fitting in flawlessly. This in important to prevent any damage from mispositioning.
- Depending on the individual, multiple visits to the dentist may be needed to assess the placement of the metal framework and the bite.
- If the bridge is a fixed type your dentist may place a temporary cement for 2 weeks, to hold it in place. And the bridge will be cemented into place.
WHAT IS THE LIFE SPAN OF A DENTAL BRIDGE?
With good oral hygiene and regular check-ups, the life span of a fixed dental bridge can go beyond 15 years. If you look after the prosthetic with great care its longevity can be extended.
WILL MY SPEECH BE AFFECTED BY THE BRIDGE?
Speaking clearly is difficult with missing teeth so a dental bridge can help this. Wearing the prosthetic with anterior teeth in their proper relationship will aid in speaking properly. The more you practice speaking, the more comfortable you will be with your prosthetic.
HOW CAN I CARE FOR MY BRIDGE?
The longevity of the dental bridge will depend on the type of material used in its fabrication and the solid foundation extended by the adjacent teeth. It’s vital to keep the remaining teeth healthy and strong too.
Take necessary precautions like brushing teeth twice daily, flossing regularly and using an antiseptic mouthwash to keep tooth decay and gum disease at bay. Your dentist will advise you on how to look after your bridge and teeth, he will demonstrate the proper technique of flossing and brushing teeth.
Stick to a regular cleaning schedule with daily visits to the dentist, this can help diagnose impending problems and treatment can be initiated before any serious damage is done.
Eating a balanced, healthy diet is also important for good gums and teeth. Food rich in calcium, iron, vitamin B complex etc. Will promote healthy gums and teeth.


